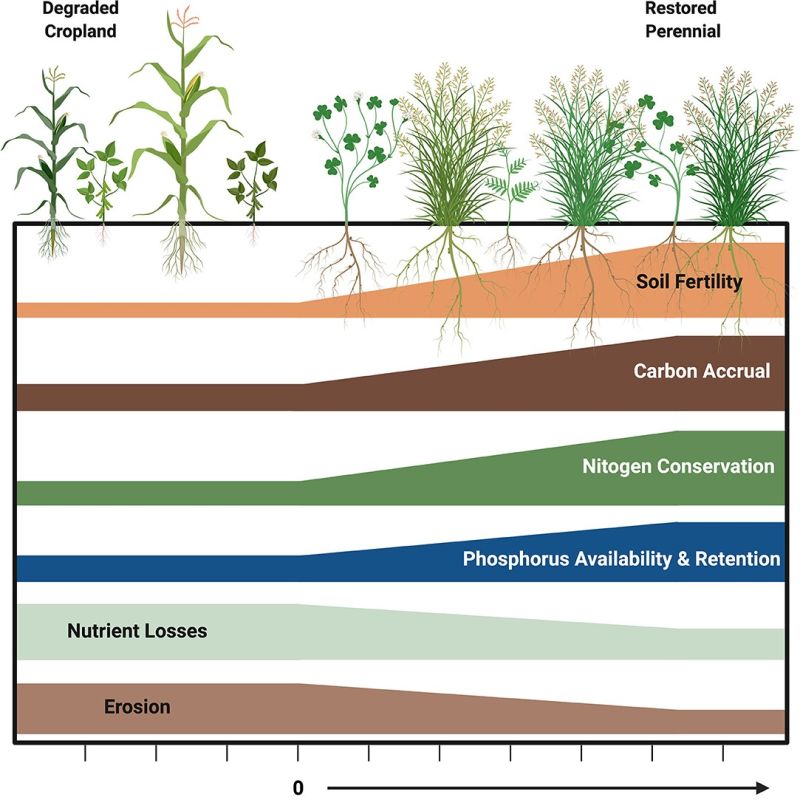
Degraded lands have a large potential for restoration via perennial cropping systems that can simultaneously provide additional ecosystem services.
The advantages of introducing perennial crops for restoring soil fertility:
-> earlier growth establishment from organs of perennation than annual plants,
-> providing permanent soil cover and influence on soil structure via deeper root systems,
-> improved carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) cycling,
-> inhibition of nutrient loss and soil erosion,
-> improved water retention (5x larger water retention potential from precipitation),
-> increased benefits resulting from microbial symbioses.
Long-term benefits of crop perennialization:
-> climate mitigation (cellulosic bioenergy),
-> sustainable animal production (rotational grazing),
-> biodiversity conservation (natural ecological succession).
Continuously growing pressure to increase food, fiber, and fuel production to meet worldwide demand and achieve zero hunger has put severe pressure on soil resources. Abandoned, degraded, and marginal lands with significant agricultural constraints—many still used for agricultural production—result from inappropriately intensive management, insufficient attention to soil conservation, and climate change. Continued use for agricultural production will often require ever more external inputs such as fertilizers and herbicides, further exacerbating soil degradation and impeding nutrient recycling and retention. Growing evidence suggests that degraded lands have a large potential for restoration, perhaps most effectively via perennial cropping systems that can simultaneously provide additional ecosystem services. Here we synthesize the advantages of and potentials for using perennial vegetation to restore soil fertility on degraded croplands, by summarizing the principal mechanisms underpinning soil carbon stabilization and nitrogen and phosphorus availability and retention. We illustrate restoration potentials with example systems that deliver climate mitigation (cellulosic bioenergy), animal production (intensive rotational grazing), and biodiversity conservation (natural ecological succession). Perennialization has substantial promise for restoring fertility to degraded croplands, helping to meet future food security needs.